The science of diamonds delves into the intricate processes behind the formation of these precious gemstones, the unique crystal structure that gives them their exceptional properties, and the various uses of diamonds in industry and jewelry. From the depths of the Earth’s crust to cutting-edge technology, this guide offers a comprehensive look at the fascinating world of diamonds.
This article will explore the formation, structure, and properties of diamonds in order to better understand their unique qualities. By learning more about the science behind diamonds, we can gain a greater appreciation for these precious and majestic gems.

Definition of Diamonds
A diamond is a naturally occurring mineral composed of pure carbon atoms arranged in a specific crystal structure. Diamonds are known for their exceptional hardness, making them one of the most durable materials on Earth. They are also highly valued for their beauty and rarity, making them popular choices for jewelry and other decorative items.
Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth’s crust, typically in the upper mantle, under high pressure and high-temperature conditions. These conditions cause the carbon atoms to bond together in a unique crystal structure known as a diamond lattice. This lattice, along with the mineral’s exceptional hardness, is what gives diamonds their unique properties.
Diamonds can come in a variety of colors, including the traditional clear or white, as well as yellow, pink, blue, and even black. The color of a diamond is determined by impurities or structural defects in the crystal lattice.
Overview of the Science of Diamonds
The science of diamonds is divided into two main areas: crystallography, which studies the structure and symmetry of diamond crystals, and geology, which focuses on how diamonds form. Crystallographers study the diamond lattice to understand its unique properties and determine how it contributes to a diamond’s strength and hardness.
. The color of a diamond is determined by how many impurities or structural defects the crystal lattice contains; the less impure, the whiter the diamond appears. Diamonds are found in a variety of geological settings, which can affect their color and clarity.
Overall, the study of diamonds is complex but fascinating. From their formation deep within the Earth’s mantle to their dazzling beauty in jewelry, diamonds are truly remarkable gems that have captivated people for centuries. With a better understanding of the science behind them, we can appreciate these gems even more.

Formation and Structure of Diamonds
The formation and structure of diamonds are closely related, with the unique crystal structure known as a diamond lattice playing a significant role in the properties of these precious gemstones. Diamonds are formed deep within the Earth’s crust, typically in the upper mantle, under high pressure and high-temperature conditions.
The carbon atoms in diamonds are bonded together through strong covalent bonds, forming a crystal structure that is highly stable and durable. This crystal structure, known as a diamond lattice, is composed of carbon atoms arranged in a specific pattern, with each atom bonded to four neighboring atoms. The diamond lattice is responsible for many of the exceptional properties of diamonds, including their exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and high refractive index.
In addition to their unique crystal structure, diamonds can also contain impurities and structural defects, such as nitrogen or boron atoms, which can affect their color and other properties. These impurities and defects are responsible for the different colors of diamonds, such as yellow, pink, blue, or black. Some diamonds can also contain trace elements such as nickel, silicon, or hydrogen.

Different Types of Diamond Formations
Diamonds can be formed in various ways and has different characteristics and properties. Here’s a list of the different types of diamond formations:
| Types of Diamond Formations | Characteristics |
| Kimberlite-hosted diamonds | These diamonds are formed in volcanic pipes known as kimberlites and are the most common type of diamond found in commercial mines. |
| Lamproite-hosted diamonds | These diamonds are formed in rare volcanic rocks called lamproites and are typically smaller and less abundant than kimberlite-hosted diamonds. |
| Placer diamonds | These diamonds are found in stream gravels and alluvial deposits and are believed to have been transported by erosion and weathering from a primary source. |
| Impact-related diamonds | These diamonds are formed by the high pressure and temperature generated by meteorite impacts and are typically small in size. |
| Marine-transported diamonds | These diamonds are formed under the ocean floor and are transported to the surface by plate tectonics. |
| Synthetic diamonds | These diamonds are created in a laboratory using various techniques such as chemical vapor deposition and high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) methods. |
| Carbonado diamonds | These diamonds are dark-colored, porous, mostly found in Central Africa and Brazil, and are believed to have formed in a unique high-pressure environment. |
Properties of Diamonds
Their unique properties come from their formation, structure, and composition – all of which contribute to their highly coveted qualities. Here we explore some of the key features that make diamonds so special.
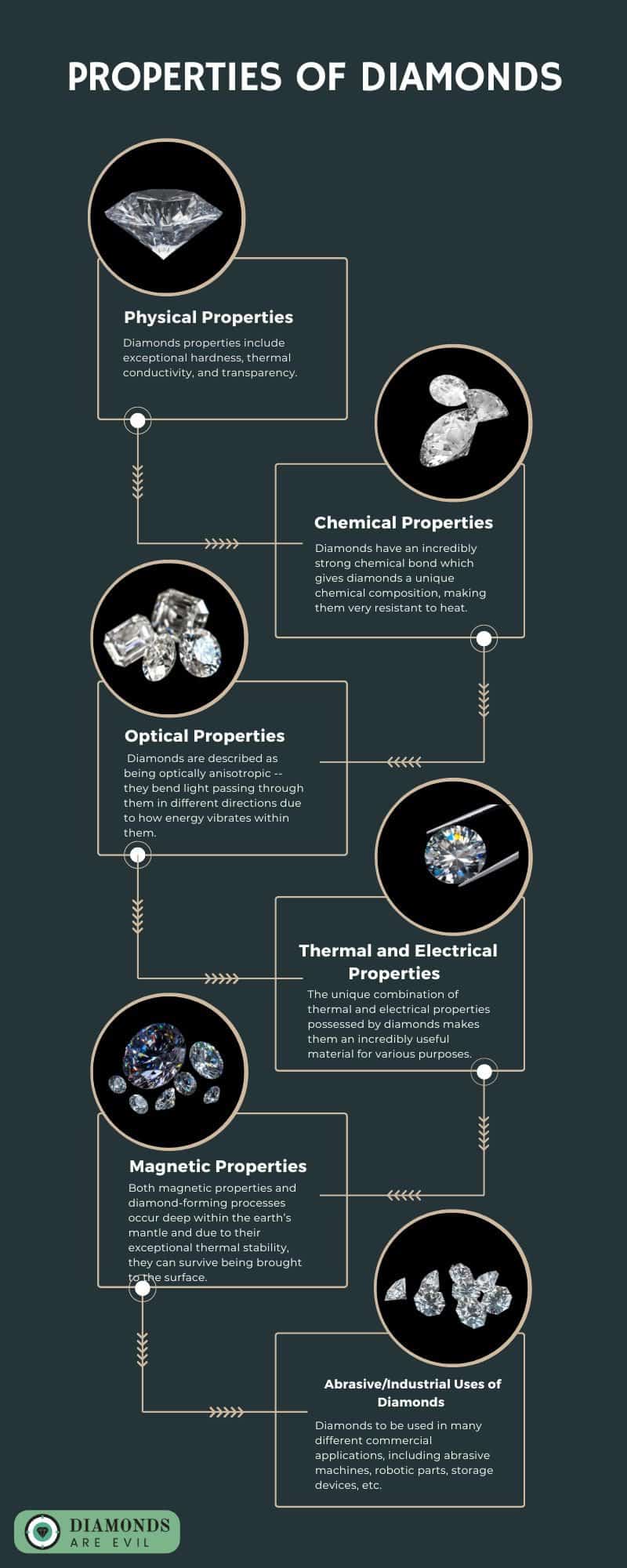
Physical Properties
The physical properties of diamonds are highly valued and are the reason they are used in many different applications. These properties include exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and transparency.
Chemical Properties
Chemical properties are important when it comes to diamonds and their various uses. Diamonds have an incredibly strong chemical bond, which makes them extremely hard and durable. This bond also gives diamonds a unique chemical composition, making them very resistant to heat and other elements that could potentially break down the stone.
Further, diamonds can act as a catalyst for certain types of reactions due to chemical characteristics such as high electron affinity and low ionization potential. Furthermore, each individual diamond’s chemical makeup is unique, giving rise to its many varied shades, tints, and tones.
Optical Properties
Diamond’s optical properties make them unique gemstones, giving them a special place in jewelry making and other special applications. Diamonds are described as being optically anisotropic — they bend light passing through them in different directions due to how energy vibrates within them.
This property is what gives diamonds their dazzlingly reflective sparkle when the light hits them just right. Because of the complexity of this process, synthetic diamonds with poor optical properties cannot replicate the crazy shapes created within natural diamond gems.
Thermal and Electrical Properties
The unique combination of thermal and electrical properties possessed by diamonds makes them an incredibly useful material for various purposes. Their ability to retain heat energy and conduct electricity has led to them becoming a popular commodity in engineering and industry.
Scientists highly value diamond’s closed-shell electron structure, which allows it to not only resist damage from humidity and acidity but also makes them ideal for use in advanced electronics like spintronics.
Magnetic Properties
Magnetic properties and properties of diamonds have fascinated individuals for centuries. Oftentimes, these two phenomena are thought of as unrelated, however, they actually have a lot of similarities. Both magnetic properties and diamond-forming processes occur deep within the earth’s mantle and due to their exceptional thermal stability, they can survive being brought to the surface.
Scientists use these phenomena to explore our planet’s history and how it has changed over time.
Abrasive/Industrial Uses of Diamonds
Diamonds have a variety of uses, but their unique properties make them particularly useful in industrial and abrasive applications. One of the most important qualities that diamond possesses is its extreme hardness: It ranks as the hardest mineral known to man. This makes diamond an ideal material for many industrial uses, such as cutting tools, abrasives for polishing and engraving, and even drilling rock.
In conclusion
Diamonds are truly remarkable gems with many unique and fascinating properties. From their formation deep within the Earth’s mantle to their dazzling beauty in jewelry, diamonds demonstrate just how powerful nature can be.
Their strength and longevity make them highly sought after in the world of fine jewelry and industrial applications alike. With a better understanding of the science behind diamonds, we can gain a greater appreciation for these precious and majestic gems.